Selenium笔记 - 基础知识
Selenium
Selenium是针对Web应用的开源自动化测试工具。包括:
-
Selenium IDE:是一个用于录制/回放测试脚本的Firefox附加组件,录制的脚本可以生成基于Selenium RC的测试代码(Java、Ruby、C#等)。
-
Selenium RC:RC由Server和Client组成两部分组成,Server负责加载/关闭浏览器以及作为HTTP代理来访问Web应用,Clinet支持多种编程语言和测试框架(TestNG、JUnit、NUnit等)。
-
Selenium WebDriver:WebDriver作为Selenium2的核心特性提供比RC更简洁易用的API,是官方推荐的RC替代方案。可以更好的支持动态网页,不需要再额外启动一个独立的Server。
-
Selenium Grid:是Selenium的一个扩展工具,可以很方便地同时在多台机器上和异构环境中并行运行多个RC或WebDriver用例。
Selenium WebDriver(Python)
安装
pip install -U selenium
API
http://seleniumhq.github.io/selenium/docs/api/py/api.html
使用
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
# start a browser
# or use Chrome, search and download chromedriver file and put it to you folder in OS path, `driver = webdriver.Chrome()`
# or use phantomjs, download it and then sepcify its path: `driver = webdriver.PhantomJS(executable_path=r'D:\phantomjs-2.1.1-windows\bin\phantomjs.exe') `
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('http://cn.bing.com')
#refresh
driver.refresh()
#find element
# find\_element and find\_elements
driver.find_element_by_id('scpl0')
driver.find_element(By.ID,'scpl0')
driver.find_element_by_name('xx')
driver.find_element(By.NAME,'xx')
driver.find_element_by_class_name('sc_hl1')
driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME,'sc_hl1')
driver.find_element_by_tag_name('body')
driver.find_element(By.TAG_NAME,'body')
driver.find_element_by_link_text('Images')
driver.find_element(By.LINK_NAME,'Images')
driver.find_element_by_partial_text('Online')
driver.find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT,'Online')
driver.find_element_by_css_selector('#scpl0')
driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR,'#scpl0')
driver.find_elements_by_xpath('//input')
driver.find_elements(By.XPATH,'//input')
# get element's attribute
element.get_attribute('href')
# play with element
element.click()
# except click, other aciton need import ActionChains class
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
chain = ActionChains(driver)
chain.context_click(element).perform()
chain.double_click(element).perform()
chain.move_to_element(element).perform()
chain.drag_and_drop(source_element, target_element).perform()
# keyboard
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
element.send_keys('xxx')
element.send_keys(Keys.ENTER)
element.send_keys(Keys.TAB)
element.send_keys(Keys.BACKSPACE)
element.send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'a') #ctrl+a
element.clear()
element.submit()
#select
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import Select
select = Select(driver.find_element_by_tag_name('select')
select.deselect_all() #<select name="" multiple>
select.select_by_visible_text('IT360')
select.select_by_index(3)
select.select_by_value('IT360')
#alert dialog
alert = driver.switch_to.alert
alert.accept()
alert.dismiss() #confirm() prompt()
alert.send_keys('haha') #prompt()
alert.text
#execute javascript
driver.execute_script('alert("hh")')
driver.execute_script('return $(".className")') #get a WebElement object
js1='document.body.scrollTop=0' # scroll to top
js2='document.body.scrollTop=10000' #scroll to bottom
driver.execute_script(js1)
driver.execute_script(js2)
#window handle
driver.switch_to.window(driver.window_handles[1])
# frame
driver.switch_to_frame('f1') # iframe's id is 'f1'
#Explicit wait and its condition
element = WebDriverWait(driver,10).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID,'xxxx')))
# more condition refer: http://seleniumhq.github.io/selenium/docs/api/py/webdriver_support/selenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.html#module-selenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions
# the way to handle alert : 1 catch UnexpectedAlertPresentException
try:
driver.get(courseurl)
time.sleep(3)
except selenium.common.exceptions.UnexpectedAlertPresentException, e:
print 'I got alert exception at location 1'
alert = driver.switch_to.alert
alert.accept()
# the way to handle alert : 2 Explicit wait
driver.execute_script('window.setTimeout ( function() { alert ("Test"); }, 3000);')
time.sleep(1) # this sleep is a workabroud for selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException: Message: unknown error: unhandled inspector error: {"code":-32000,"message":"Could not handle JavaScript dialog"} # https://bugs.chromium.org/p/chromedriver/issues/detail?id=1633#c4 # https://bugs.chromium.org/p/chromedriver/issues/detail?id=1500
alert = WebDriverWait(driver, 5).until(EC.alert_is_present())
if alert:
myLogger.info(u'--- Expected alert appeared:{}'.format(alert.text))
alert.accept()
#Implicit Wait
driver.implicitly_wait(5)
#Driver
driver.maximize_window()
driver.set_window_size(800,600)
driver.title
driver.current_url
driver.back()
driver.forward()
#Cookie, get cookies
for cookie in driver.get_cookies():
print '%s -> %s' % (cookie['name'],cookie['value'])
#Cookie, get a cookie
driver.get_cookie('cookiename')
#Cookie, add a cookie
driver.add_cookie({'name':'key','value':'value','path':'/'})
#Cookie, delete a cookie
driver.delete_cookie('cookiename')
#Cookie, delete all cookies
driver.delete_all_cookies()
#change user-agent
profile = webdriver.FirefoxProfile()
profile.set_preference('general.useragent.override',"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; Intel Mac OS X 10.11; rv:45.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/45.0")
#Get html code of a element
element.get_attribute('innerHTML')
#WebDriver default timeout <https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17533024/how-to-set-selenium-python-webdriver-default-timeout> <https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30114976/the-default-value-of-timeouts-on-selenium-webdriver>
driver.set_page_load_timeout(30) #This will throw a __TimeoutException__ whenever the page load takes more than 30 seconds.
#Reload page and open new page by js
driver.execute_script('location.reload();location="http://cn.bing.com"')
Selenium IDE
安装
在这里下载安装Firefox的Selenium IDE插件。
使用
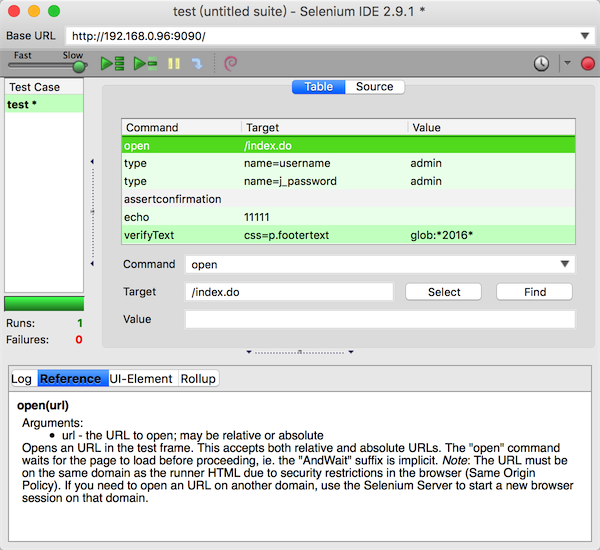
测试的每一步是一个命令,由Command、Target和Value组成。Command是具体操作,比如打开(open)一个页面、检查页面中文字(verifyText)等等。Target和Value是command的参数,分别表示要操作的对象和其值。
录制一个测试用例很简单,点击红色录制按钮即可。操作会自动记录下来。
录制的过程中,如果要对某个文字进行操作,比如验证是否匹配正则表达式,在浏览器中右键菜单中就有可用的Selenium IDE命令了。
录制完成后可以编辑每个命令。
录制后的测试用例可以保存为html文件,供以后导入到Selenium IDE。或者导出为其他语言程序,例如python。
Command
使用verify还是assert?
verify即使失败还会继续执行后面的命令。
assert失败后退出测试用例。
一般集合二者使用。一个assert后面跟一个或多个verify。
常用命令:
-
open(url)
接收一个参数url,即command=open, target=url
-
type(locator,value)
给locator指定的元素或属性赋值以value
-
click(locator)
单击一个链接、按钮、checkbox或radio等等,locator即元素定位
-
clickAndWait(locator)
单击一个链接、按钮等等元素,单击后等待新的页面加载
我们的表单提交,就可以用这个方法来单击submit按钮。
类似的方法还有selectAndWait、typeAndWait、focusAndWait…… -
verifyLocation(pattern)
校验当前页面的绝对路径(url)是否与pattern匹配,关于pattern的解释,我们在下面具体说明。
-
verifyValue(locator, pattern)
校验指定元素的值是否与指定pattern匹配
-
verifyVisible(locator)
校验指定元素是否可见,如果当前元素的style=”display:none”,即不可见。
-
verifyTextPresent(pattern)
校验当前页面是否出现该文字
-
verifyChecked(locator)
用于校验checkbox是否被选中
-
verifyAttribute(locator, pattern)
校验指定的元素属性值,是否匹配pattern
例如:verifyAttribute(link=All Search Results for “bike”@href, ‘glob:*/search/bike?c=0’)
即校验指定的link的href属性是否匹配”glob:/search/bike?c=0*” -
fireEvent(locator,eventName)
用于调用locator指定的元素的指定eventName的事件,例如:
fireEvent(userLoginName,blur),即调用文本框userLoginName的失去焦点事件
Target
就是在页面中选择要操作的对象。有以下几种方式:
-
默认是“标识符”:就是html标签的id和name属性值。例如
loginForm -
使用id。比“标识符”更具体。例如
id=loginForm -
使用name。比“标识符”更具体。例如
name=continue -
使用xpath。例子:
xpath=/html/body/form[1]- 绝对路径//form[1]- HTML中的第一个表单xpath=//form[@id='loginForm']- id为loginForm的表单xpath=//form[input/@name='username']- 第一个表单:有input子元素,而且input的name属性为username//form[@id='loginForm']/input[4]- id为loginForm的表单的第十个input。注意和上一条的区别。//input[@name='username']- name为username的第一个input//form[@id='loginForm']/input[1]- id为loginForm的表单的第一个input//input[@name='continue'][@type='button']- 第一个name为continue而且type为button的input
-
使用超链接文本。例如
link=Cancel -
使用DOM。例子:
- dom=document.getElementById(‘loginForm’)
- dom=document.forms[‘loginForm’]
- dom=document.forms[0]
- document.forms[0].username
- document.forms[0].elements[‘username’]
- document.forms[0].elements[0]
- document.forms[0].elements[3]
-
使用CSS。例子:
- css=form#loginForm
- css=input[name=”username”]
- css=input.required[type=”text”]
- css=input.passfield
- css=#loginForm input[type=”button”]
- css=#loginForm input:nth-child(2)
css比xpath更快。而且可以定位更复杂的元素。
以
//开头的为xpath,所以可以省略xpath=;以document开头的为DOM,所以可以省略dom=
Value
type命令对应具体字符串。当验证的时候(verifyTextPresent、verifyTitle、verifyAlert、assertConfirmation、verifyText或verifyPrompt),可使用通配符、正则表达式和精准文本。
-
通配符
-
前缀为
glob: -
* :任意字符
-
[] :字符集合中的任意一个,例如
[a-zA-Z0-9] -
不支持
?号
-
-
正则表达式
- 前缀为
regexp:区分大小写;regexpi:不区分大小写
- 前缀为
-
精准文本
- 前缀为
exact:或不写
- 前缀为
-
没有写前缀的时候,默认使用
glob:
存储的值
在前面命令存储,供后面命令使用。例如:
| command | target | value |
|---|---|---|
| store | paul@mysite.org | userName |
使用:${value}
| command | target | value |
|---|---|---|
| verifyText | //div/p | ${userName} |
javascript使用:storedVars[‘yourVariableName’]
| command | target | value |
|---|---|---|
| store | 10 | hits |
| store | Edith Wharton | name |
| store | league of nations | searchString |
| storeXpathCount | //blockquote | blockquotes |
| storeEval | storedVars[‘hits’]-storedVars[‘blockquotes’] | paragraphs |
| storeEval | storedVars[‘name’].toUpperCase() | uc |
| storeEval | storedVars[‘name’].toLowerCase() | lc |
| type | q | javascript{storedVars[‘searchString’].toUpperCase()} |
弹出窗口 alert/confirm/prompt
通用命令:(verify|assert)(alert|confirm|prompt),(verify|assert)(alert|confirm|prompt)(Present|NotPresent)
各自命令:
alert
| command | target | value |
|---|---|---|
| open | / | |
| click | btnAlert | |
| assertAlert | I’m blocking! | |
| verifyTextPresent | Alert is gone. |
confirm
| command | target | value |
|---|---|---|
| open | / | |
| click | btnConfirm | |
| chooseCancelOnNextConfirmation | ||
| assertConfirmation | Choose an option. | |
| verifyTextPresent | Rejected |
prompt
| command | target | value |
|---|---|---|
| open | / | |
| answerOnNextPrompt | Selenium! | |
| click | id=btnPrompt | |
| assertPrompt | What’s the best web QA tool? | |
| verifyTextPresent | Selenium! |
Selenium RC
Selenium RC架构图:
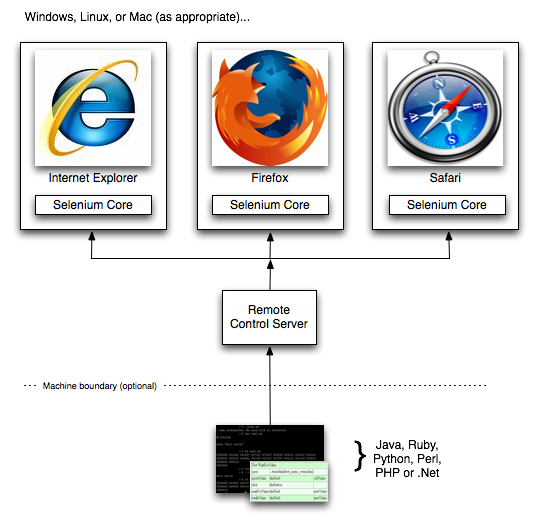
Selenium RC的具体使用见: